Ice and Stone
Comet of the Week: The Daylight Comet of 1910
Perihelion: 1910 January 17.59, q = 0.129 AU In early 1910 the entire world – astronomers and lay public alike – awaited the imminent return of Comet 1P/Halley, which had been recovered the previous September and which was already detectable with moderate-sized telescopes. While Halley would go on to put on a spectacular display around …
Special Topic: Exocomets
It is now generally accepted that the planets in our solar system formed via the accumulation of smaller bodies dubbed “planetesimals” – which in turn formed from the accumulation of dust grains and (in the outer and thus colder regions) gas molecules – early in its history. Due to the early sun’s rotation the infalling …
This Week in History: January 19-25
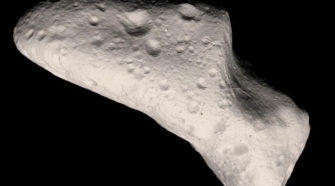
JANUARY 19, 2006: NASA’s New Horizons mission is launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida. After a somewhat distant flyby of the main-belt asteroid (132524) APL in June 2006 and a gravity-assist encounter with Jupiter in February 2007, New Horizons encountered Pluto and its system of moons in July 2015 – providing our first detailed view of …
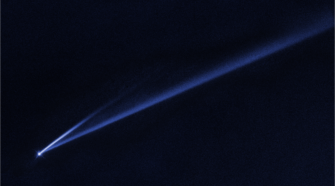
Comet of the Week: (6478) Gault
Perihelion: 2020 January 2.79, q = 1.859 AU It has been obvious for several decades that the dividing line between “comets” and “asteroids” is, in a word, nebulous, and some facets of this will be explored in future “Special Topics” presentations. One group of objects that are included within this discussion were initially referred to …
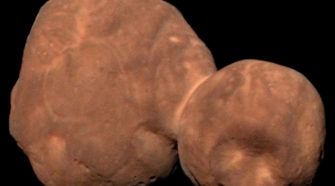
Special Topic: Asteroid (433) Eros
Two weeks ago I devoted the “Special Topics” presentation to the subject of near-Earth asteroids. Up until almost the end of the 19th Century all of the over 400 asteroids that had been discovered up to that time orbited within the “main asteroid belt” between Mars and Jupiter, and the astronomers of that era were …
This Week in History: January 12-18
JANUARY 12, 1910: A group of diamond miners in the Transvaal in South Africa spot a brilliant comet low in the predawn sky. This was the first sighting of what became known as the “Daylight Comet of 1910” (old style designations 1910a and 1910 I, new style designation C/1910 A1). It soon became one of …